
Histology
Indication
Technique used for microscopic study of tissues.
Test description
Tissue sections cut and stained with different histological stains such as: Hematoxylin & Eosin, Alcian Blue, Congo Red, Giemsa, Masson’s Trichrome, PAS, Reticulin, Thioflavin or Ziehl-Neelsen.
Histological techniques
- Additional slides unstained
- Antigen retrieval+Deparaffinization
- H&E/NFR stain on precut slides
- Hematoxylin & Eosin
- Human bone marrow decalcification
- Mouse decalcification
- Nuclear fast red
- Paraffin sections for PCR
- Serial sections
- Special Stains in Histology-H
Inmunohistochemistry
Indication
Technique that is used to determine the expression of certain proteins in a specific tissue.
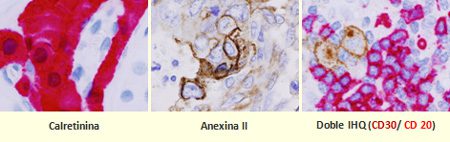
Description of the Technique
Tissue sections are performed and the expression of proteins is determined using specific antibodies. The whole process is automated.
The advantage of using different enzymes such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or alkaline phosphatase (AP) with specific chromogenic (DAB, Fast Red, etc) allows us to do double staining in order to analyze colocalization of different proteins.
The Unit has 3 platforms: Dako-Autostainer Plus, Leica-Bond MAX and Roche-BenchMark Ultra, which allow to adapt the best protocol for each antibody.
- Available antibodies (human samples)
- Available Techniques (Mouse Samples): Antibodies
- Available panels (in Spanish)s
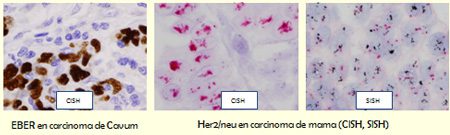
Chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH)
Indication
In situ hybridization techniques involve the detection of specific nucleic acid sequences (DNA or RNA) inside the cells, using specific probes marked.
EBER probe is used for the identification of latent infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) associated with several diseases, such as: Hodgkin’s lymphoma, B cell lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, gastric carcinoma and others.
Kappa and Lambda probes are used for identification of mRNA from Kappa and Lambda light chains from the immunoglobulins of B cells.
The HER2 gene is amplified and over-expressed in invasive forms of breast cancer, uterine cancer, ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer, gastric cancer, prostate cancer and osteosarcoma. It represents a predictive factor of the therapeutic efficacy with the monoclonal antibody Trastuzumab (Herceptin).
Chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH)
ALU Positive Control Probe II
Description of the technique
EBER, Kappa and Lambda probes are labeled with fluorescein and used with the Vision Biosystems automated system (Bond) with DAB chromogenic visualization.
HER2 CISH Kit is a two-color signal chromogenic visualization, obtained with specific probes for the HER2 gene (red signal) and the centromeric region of chromosome 17 (blue signal). It uses a mixture of DNA probes labeled with Texas red for the HER2 gene, and a mixture of fluorescein-labeled PNA probes for the centromeric region of chromosome 17 (CEN-17).
In the SISH method, the HER2 gene is detected by hybridization with a labeled DNA probe with Dinitrophenol (DNP) and visualization with silver, followed by hybridization with the centromere CEN17 probe, labeled with DNP and visualization with Fast Red.
Tissue MicroArrays
Indication
This technique allows the simultaneous analysis of multiple samples of tissue integrated into a single paraffin block, enabling the monitoring of expression of hundreds of tissue samples or tumor samples in a single experiment. This ensures the homogeneity of results between samples and a considerable saving of time and reagents.
Some of the applications of this technique are the following:
- Adjustment of new molecular markers with prognostic value.
- Quality control of immunohistochemical techniques and in situ hybridization.
- Optimization of antibodies and probes.
- Validation of data obtained from cDNA microarrays.
- Simultaneous and massive analysis of the molecular profile of a large number of tumors.
Description of the technique
A recipient paraffin block is made where we place the cores of the samples that we want to analyze. We should select the diameter of the core (0.6, 1, 1.5 or 2mm) and, depending on this, we can include up to 400 cores or samples in the same block. This TMA block can be cut with the same method (at 3um with waterbath) that is used for histological, IHC and in situ hybridization techniques.
- It is important to select donor blocks with more than 2mm depth tissue.
- If the donor block is very wasted and has not enough paraffin, it would be convenient to remake the block with new paraffin.
- It is necessary to make a recent HE stain of the donor blocks and select the area with a permanent pen.
- An excel file including all the samples should be enclosed to the TMA.
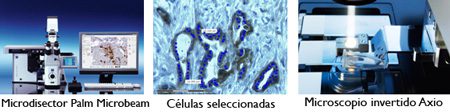
Laser microdissection (LMD)
Indication
The tissue microdissection method consists of sorting small areas or independent cells from a complete tissue section embedded in paraffin or a frozen tissue, obtaining pure cellular populations and extracting DNA, RNA and proteins.
Description of the technique
The equipment used, Zeiss PALM microbeam, is based on the Axio Observer inverted microscope fromCarl Zeiss that is controlled by Palm-microbeam software. The main feature of this tool is an N2 laser (“cold laser” ? = 337nm), that works at different wavelengths to UVA, thus avoiding damage to the DNA of microdisected cells. The laser goes through the microscope objectives and only cuts the area selected for the study, the rest of the sample is not affected and it is not possible to change the sub cellular structures. After microdissection, samples are catapulted directly in the cap of the eppendorf.
References
- Cano I, Lozano M, Rodríguez A, Mate A, Adrados M, López Mdel M, Carro R, Montes-Moreno S. Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma and T cell histiocyte-rich large B cell lymphoma: diagnosis in two monozygotic twins. Histopathology. 2010 Jul;57(1):159-62
- Guerra C, Collado M, Navas C, Schuhmacher AJ, Hernández-Porras I, Cañamero M, Rodriguez-Justo M, Serrano M, Barbacid M. Pancreatitis-induced inflammation contributes to pancreatic cancer by inhibiting oncogene-induced senescence. Cancer Cell. 2011 Jun 14;19(6):728-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.05.011.
- Delgado-Calle J, Sañudo C, Sánchez-Verde L, García-Renedo RJ, Arozamena J, Riancho JA. Epigenetic regulation of alkaline phosphatase in human cells of the osteoblastic lineage. Bone. 2011 Oct;49(4):830-8. Epub 2011 Jun 13.
- Adjuntar un listado Excel con las muestras a incluir.
Image Analysis
Ariol Applied Imaging Equipment
The image analysis system Ariol is an automated system developed to quantify different markers from immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescen. Once the slide of interest is scanned using the software Ariol, the following performances will take place: quantifications of nuclear, membrane and cytoplasm markers, cell counting, measuring of vessel density both in histological and immunohistochemistry sections and in tissue microarray.
This system is very useful for diagnosis and research and due to its flexibility can be adapted to many quantitative and qualitative analysis.

References
- Aggarwal M, Villuendas R, Gomez G, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Sanchez-Beato M, Alvarez D, Martinez N, Rodriguez A, Castillo ME,Camacho FI, Montes-Moreno S, Garcia-Marco JA, Kimby E, Pisano DG, Piris MA. TCL1A expression delineates biological and clinical variability in B-cell lymphoma. Mod Pathol. 2009 Feb;22(2):206-15. Epub 2008 Sep 26.
- Wahlin BE, Aggarwal M, Montes-Moreno S, Gonzalez LF, Roncador G, Sanchez-Verde L, Christensson B, Sander B, Kimby E. A unifying microenvironment model in follicular lymphoma: outcome is predicted by programmed death-1–positive, regulatory, cytotoxic, and helper T cells and macrophages. Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jan 15;16(2):637-50. Epub 2010 Jan 12.
- Matheu A, Collado M, Wise C, Manterola L, Cekaite L, Tye AJ, Canamero M, Bujanda L, Schedl A, Cheah KS, Skotheim RI, Lothe RA,López de Munain A, Briscoe J, Serrano M, Lovell-Badge R. Oncogenicity of the developmental transcription factor Sox9. Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 1;72(5):1301-15. Epub 2012 Jan 13.
Dotslide
DotSlide is an imaging system for ‘virtual microscopy’ that consists of the Olympus BX51 microscope, bright field, whose components are fully motorized and controlled by an image capture software that monitors and automates the scanning process, allowing the creation of digital slides. Viewer software can be viewed with the same precision than the microscope on any computer. In addition the system can also perform morphometric studies and estimate of areas. This digital virtual microscopy image can be saved in a web-based database and is accessible for online conferencing, e.g. in pathology or histology.
